Whale shark (Rhincodon typus) – the largest fish in the world
20 meters (66 ft) of length, 25 tons of weight – here comes the biggest fish in the world – the whale shark. Every era had its own giant. Today we also take pride in several gigantic land animals (African bush elephant), birds (harpy eagles, pelicans, albatrosses) or water organisms (blue whale). When considering the last group of animals, it is worth taking a special note of the whale shark – the largest fish of today`s world, and one of the most mysterious and beautiful creatures (un)known by humankind at the same time.
Classification
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Order: Carpet sharks (Orectolobiformes)
- Family: Rhincodontidae
- Genus: Rhincodon
- Species: Whale shark (Rhincodon typus)

Areas of occurrence
Whale shark is not an animal bound by a certain area – it relocates eagerly. It is told to be a ‘cosmopolitan’ species – it appears in almost every tropical and subtropical waters, besides the Mediterranean Sea. It is common in the open seas as well as near-river areas and cold sea currents areas. It has been observed that these enormous fish appear repeatedly in the same spots during certain seasons of the year. It is highly plausible that it is linked with finding vast quantities of plankton which is their food, and additionally with the mating season.
Whale shark is a great attraction in the Western part of Australia. Divers can swim accompanied by those gentle giants there.

Whale shark stays mainly in the 30o North to 36.5o South latitude range. This fish inhabits most of the warm seas and oceans.
Inhabited areas
- Atlantic Ocean
- Pacific Ocean
- Indian Ocean
- Arabian Sea
- Red Sea
It is also found in shallow coastal waters, near the coral reefs.
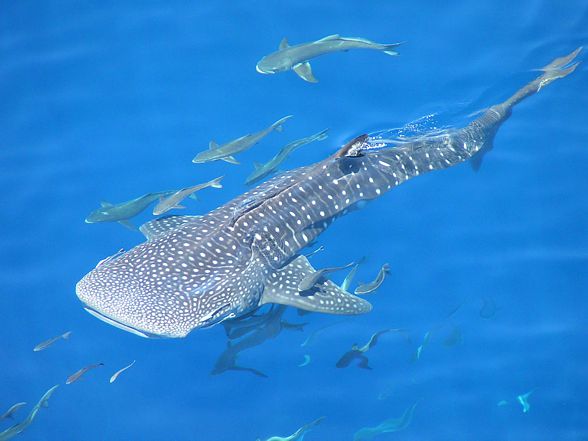

Lifestyle
The whale shark stands out as an individual among other sharks. Its cousins from the Orectolobiformes order (carpet sharks) live in the depths near the sea bottom. However the whale shark opts for the near-surface open waters. Temperature in those waters ranges from 18 to 30 oC (64 – 86 ºF). Despite its customary lifestyle, the whale shark can dive really deep – reaching depths of up to 700 meters (765 yd) is not a problem. It can stay in the depths long enough to acquire a substantial amount of food.
During migration, the whale shark covers great distances. The stretch of the starting and finishing point is measured in thousands of kilometers. The shark needs a few weeks or months to cross such vast distances. We would not be able to acquire such knowledge without the use of satellite transmitters in the East Asia.
It is has been observed that whale shark has the ability to cross 3000 km (1865 mi) in two months. One animal began its journey in the Philippines to mark its end in Vietnam. Moreover, a case of a whale shark returning to the starting point – Malaysia – after passing over 2000 km (1242 mi) was recorded. After all it is not such a big feat for a marathon swimmer like the whale shark, capable of migrating over 12 000 km (7 456 mi). Thanks to transmitters` data it has been established that these sharks only begin to migrate after reaching an adequate size – at least 5 meters (16ft 5in) of length.
Whale sharks lead a solitary lifestyle. They are active both during the day and at night.

Characteristic
Appearances
Whale sharks are absolutely stunning in terms of coloration. The main reason is the beauty of the speckles which are, interestingly, systematically arranged in lines. The back of the whale shark may be dark gray, brown or green with a slight addition of red color. Speckles are usually yellow, white and green.
The shark`s abdomen is white or greenish. Shark`s coloration develops until reaching 4 meters (13 ft) of length – then the final pattern of coloration is settled. Distinctive speckles, arranged like a checker is a unique symbol system for every whale shark.
The flattened head is accompanied by a wide mouth. Small eyes close through rolling back and withdrawing into the inside of the head. Little barbels grow out of the nasal area. The whale shark has 3 keels (tapering edges of the body) – one in the middle of its body and two in its upper area.
This fish also has a remarkably thick skin. It is rubbery and about 10 cm thick.

Distinctive features
The whale shark`s body has a streamline shape and its head is flattened. Wide mouth is located on the tip of the head – contrary to e.g. the great white shark, which mouth is located a little rearward. The dorsal fin, located closer to the head is bigger than the second one placed near the fishtail. The caudal fin is crescent-shaped.
Young whale sharks typically have the upper part of their caudal fin much larger than its lower part. An adult whale shark may reach from 15 to 20 meters (49ft 3in – 65ft 7in) of length, though these are only approximate values for the maximum length of this shark is not known. Some researchers claim that whale shark may reach up to 20 meters (65ft 7in) of length and 25 000 kg (55 000lb) of weight. However the claims are unconfirmed.
This enormous fish has around 3000 small, 6-milimeter teeth. Yet it does not use them to acquire food. The whale shark has a narrow esophagus that does not allow it to swallow a bigger catch.
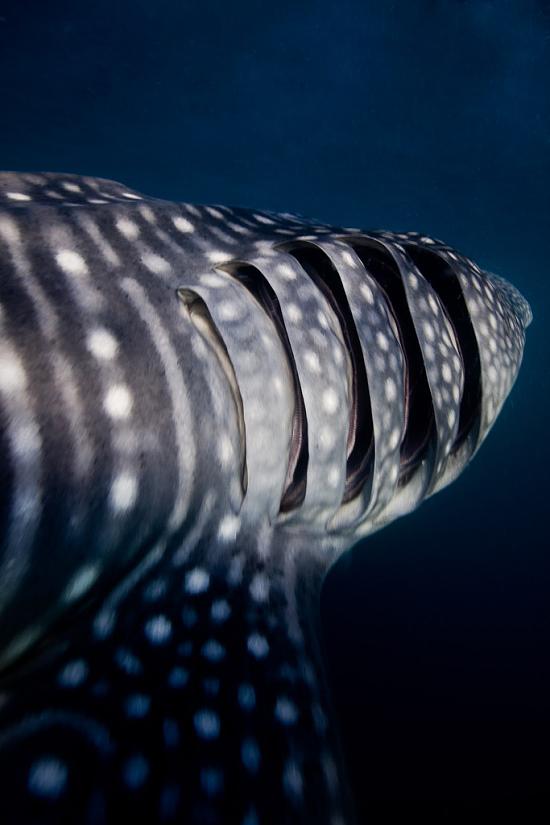

Lateral line and Ampullae of Lorenzini
In spite of the whale shark`s disparity from the rest of its predatory cousins, it also has many common features – the lateral line and Ampullae of Lorenzini, which are specially developed sensory systems. The lateral line consists of two canals located alongside the body. Inside they carry multiple sensory cells.
This system allows the fish to sense even the slightest vibration of the water. Thereby the shark can identify the size, speed and location of the object causing these vibrations. Ampullae of Lorenzini serve to detect changes in the electric field.
It is supposed that they also allow to examine water temperature, its salinity or pressure changes.
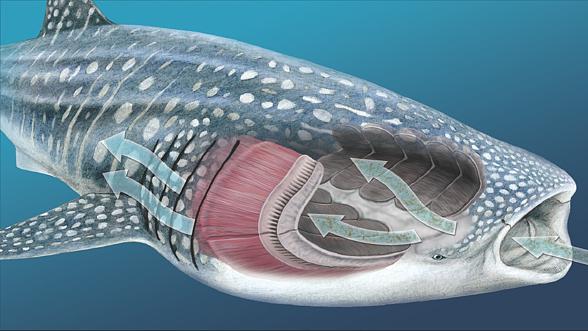
Food
Whale shark is one of the three plankton-eating sharks. Besides plankton, it also eats small fish, shellfish, sometimes cuttlefish or even tunas. Whale shark also eats phytoplankton and other underwater plants.
The mechanism of acquiring food is quite interesting – the shark may choose from two approaches: active and passive. Swimming under the water`s surface it simply opens its mouth – therefore we call it passive. Whilst wanting to acquire food actively, it sucks the water in.
Sharks may caught feasting even at dusk or at night. The shark takes up a vertical position with its head facing upwards. Next it moves upwards and downwards repeatedly in 15-20s intervals, stopping directly below the water surface, thus the water with large amounts of food flows into its mouth at great velocity.
The shark senses plankton thanks to a highly developed olfactory apparatus located at both sides of the upper lip.

Breeding
It is known for certain that whale shark is an ovoviviparous species (ovoviviparia). The female gives birth to up to 16 baby sharks. However the place of their procreation remains a mystery. It is believed that only 10% of the babies from one litter survive.
After being born the mother leaves them without patronage. As a result of small number of caught baby sharks, in terms of their maturation not much is known. Due to common knowledge baby whale sharks have ca. 55 cm (22 in) of length. Whale sharks reach sexual maturity around 25 years of age. The long maturation process affects the diminishing number of those gigantic fish.
It is believed that a whale shark can live through 100, or even op to 150 years. Much alike the longest living turtles. Most sources state that its lifespan peaks to about 70 years of age though.
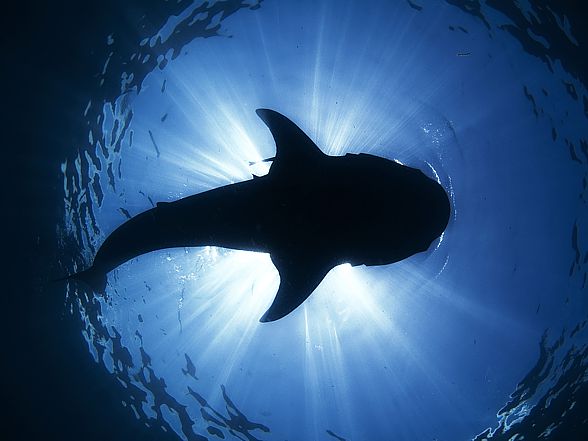

Detailed characteristic / size
Whale shark (Rhinocodon typus)
- Length: ca. 10-15 meters (33 – 49 ft), unconfirmed sources claim it to be up to 20 meters (65 ft 7.4 in). Official measurement – 12.65 m (41 ft 6.0 in).
- Weight: 10-20 tons (unconfirmed sources claim even 30 tons). Official weighting – 13.6 tons.
- Lifespan: probably up to 100 years (most sources state around 70 years).
- Lifestyle: usually solitary, seldom a whole group consisting of a few or several dozen animals is observed.

Whale shark – interesting facts. Have you known, that…
- Whale shark`s conservation status was defined as “vulnerable to threats” in the year 2000.
- Whale shark is an endangered species , thus it is covered with a worldwide protection program.
- Although it is a protected species, illegal fishing for whale sharks still takes place in Taiwan and Philippines.
- Around 100 whale sharks are killed every year in Taiwan
- Whale shark is extremely vulnerable to industrial waste and other harmful human actions.
- Whale shark is a great attraction in the Western part of Australia. Divers can swim accompanied by those gentle giants there.
- Whale shark is the only species of the Rhincodontidae family and additionally the only shark in the Elasmobranchii subclass to live in the open sea and ocean waters.
- Whale shark is a one of the few sharks eating plankton. Besides it, the basking shark (Cetorhinus maximus) and megamouth shark (Megachasma pelagios) have a similar diet.
- The goal of whale sharks` migration is not yet established. There are regions in which they turn up every year, there are also places they visit to find more food.
- Groups of whale sharks come to certain coastal areas and often stay there for a few months.
- It is not established whether both young and adult animals take part in migration.
- A whale shark can filter about 6 tons of water an hour.
- Despite its enormous size and being a shark (duh!), this exact species is remarkably friendly towards humans – it is one of the traits which makes fishing for whale sharks so easy – it is not scared by the sight of men.



















