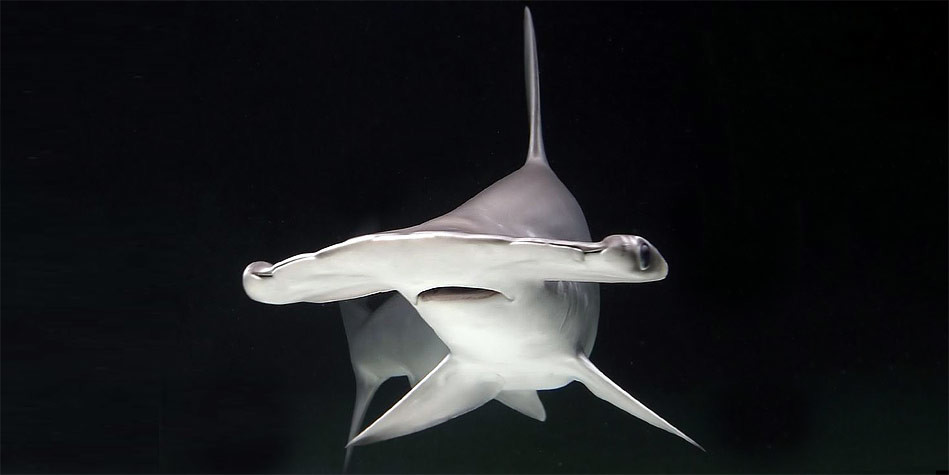
Smooth hammerhead shark (Sphyrna zygaena)
The hammerhead shark astonishes people mostly with its appearance. The first thing that strikes the eye is its head, resembling the shape of a hammer. However, this animal has much more unusual features that can be more astonishing than the head shape. These features include the 360-degree field of view or parthenogenesis, i.e. reproduction without a male’s involvement.
Name
The smooth hammerhead (Sphyrna zygaena) is also called hammerhead, common hammerhead, common smooth hammerhead, round-headed hammerhead. The name comes from the characteristic head shape resembling a hammer.
Classification
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Chondrichthyes
- Subclass: Elasmobranchii
- Superorder: Selachimorpha
- Order: Carcharhiniformes
- Family: Sphyrnidae
- Genus: Sphyrna
- Species: Smooth hammerhead (Sphyrna zygaena)

Occurrence
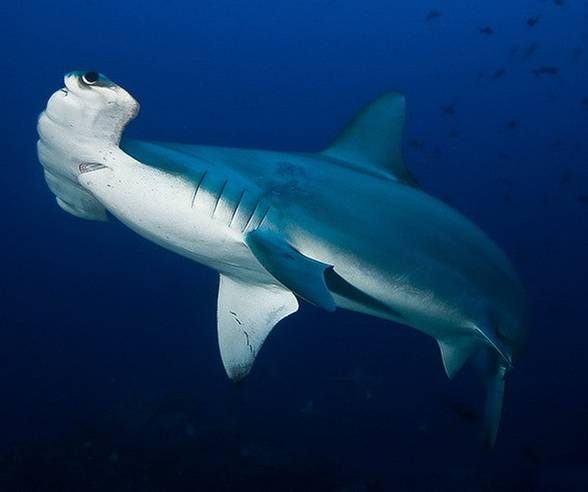
The smooth hammerhead is very tolerant of water temperature. Due to this tolerance, the shark can be found all over the world. As for the Atlantic Ocean, the shark is found in the area of New Scotland to the Virgin Islands and from Brazil to the western coast of southern Argentina. Moreover, it can be found in the waters of British Islands and Ivory Coast.
The smooth hammerhead also prefers the eastern area of the Mediterranean Sea, the Indian Ocean, waters of Southern Africa, India and Sri Lanka. It is also found in the Gulf of Tonkin, waters of southern Japan, Siberia, Australia and New Zealand.
As for the Pacific Ocean, the smooth hammerhead lives in the waters of Hawaii, California, Panama, the Galápagos Islands, Ecuador, and Chile.
It is believed that the species does not occur in tropical waters, although there have been reports of sightings hammerhead sharks in the area of Mozambique and the Gulf of Mannar belonging to India. The shark’s presence in tropical waters is difficult to determine due to the occurrence of other fish from the family Sphyrnidae.

Natural environment
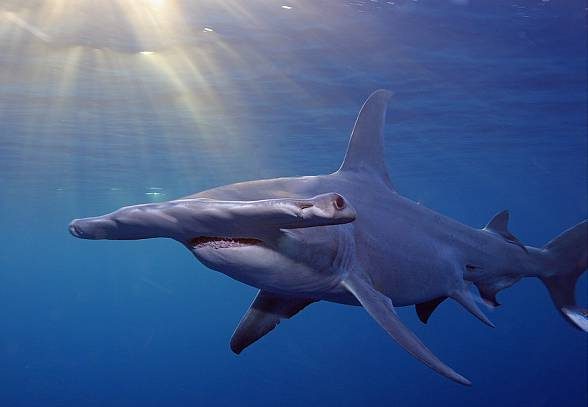
The smooth hammerhead swims quite close to the water surface – it does not go deeper than 20 meters. It prefers coastal waters, gulfs, and river mouths, but it can also be found in the open continental shelf and near oceanic islands.
However, it happens that the shark dives even 200 meters deep into the ocean.
The smooth hammerhead migrates depending on the season. In the winter, it swims towards the equator, and in the summer, it remains in cooler waters.

Characteristic features
The most characteristic feature of the smooth hammerhead is, of course, its head that has a hammer-like shape. The head has no indentation in the middle, which enables differentiating this species from other hammerhead sharks.
The eyes are situated on the sides of the head. Due to such positioning of the eyes, the field of view of the shark is 360 degrees. The shark can also see stereoscopically, i.e., it can assess the distance from its target.
Such capabilities of hammerhead sharks probably evolved as a result of its position in the food chain. The smooth hammerhead can see its prey very fast, as well as any threat.
The smooth hammerhead has from 51 to 62 teeth – each of them is triangular, with smooth or slightly uneven edges.
The first dorsal fin is moderately tall, falcate and rounded at the tip. The pectoral and pelvic fins are rather straight. The rear fin is bigger than the dorsal fin and resembles the letter “W”.
The back of the smooth hammerhead is dark brownish gray or olive (most other hammerheads have brown backs). The sides are lighter and the belly is completely white. Sometimes the edges of the pectoral fins are darker.

Diet and prey
Smooth hammerheads are active predators. They feed on fish, stingrays, cephalopods, shellfish, crabs, shrimps, and even other sharks – including their own species.
The diet of this animal also depends on the place of its occurrence. In northern Europe, its favorite food includes herring, in North America – the Atlantic Spanish mackerel, and in South Africa – squids and sardines.
Lifestyle
Smooth hammerheads are solitary or they form small groups. Larger groups are formed only for annual migrations or they concentrate young sharks that are not 1.5 m (4.9 ft) long yet. They may consist of even hundreds of individuals.
In the summer, during the heat period, the sharks swim closer to the surface, which can be observed because of the dorsal fin protruding out of the water.
The young are threatened by other shark species, and the adult sharks often become the prey of killer whales.
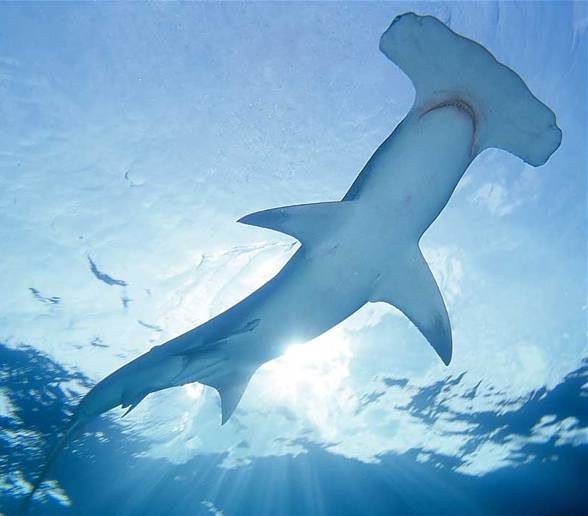

Distinctive reproduction
Female smooth hammerheads can reproduce by parthenogenesis, i.e., without a male’s involvement. Initially, it was thought that female sharks could store sperm in their bodies even for several years, however, the observations of a female in Henry Doorly Zoo in Nebraska officially confirmed the thesis about parthenogenesis.
In 2001, a female gave birth after staying in the tank with two other females for several years. Additionally, the pup was male and it had his mother’s genetic material only.
Smooth hammerheads become sexually mature at the age of 8 years. Gestation is 10-11 months and 20-50 pups are born. The delivery occurs in shallow waters, and pups are from 50 to 61 cm (20–24 in) long.
The smooth hammerhead lives over 20 years.

Sharks and people
The smooth hammerhead is a potential threat for people. In 2008, the International Shark Attack File received 34 reports about attacks, of which 17 were unprovoked by humans. One of them was fatal.
Few attacks on people may result from the type of waters inhabited by smooth hammerheads. These include quite cool bodies of water, in which people swim reluctantly.
The smooth hammerhead is also fished commercially, and its meat is sold fresh, dried, salted or smoked. In most markets, it is not, however, demanded goods – except for Asian countries. Smooth hammerheads are fished for sports also.

Detailed information / size
Smooth hammerhead (Sphyrna zygaena)
- Body length: from 2.5 to 3.5 m (8.2–11.5 ft), maximum 5 m (16 ft)
- Weight: to 400 kg (880 lb)
- Lifespan: over 20 years
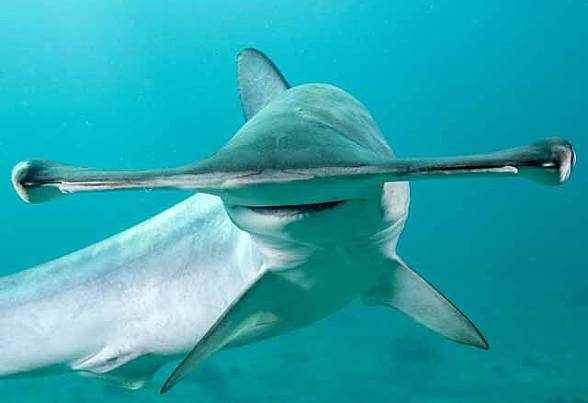

Hammerhead shark – interesting facts
- The fins of the smooth hammerhead are considered a delicacy in Asian countries, although the species itself is considered as inedible.
- Shark liver oil is considered as a source of vitamins and necessary minerals.
- The smooth hammerhead is not the only fish included in the family Sphyrnidae.
- Females of hammerheads can reproduce without a male’s involvement – a hammerhead shark born in 2001 in the Nebraska zoo was the result of a so-called virgin birth. More on this topic can be found in “Virgin birth in a hammerhead shark” – Demian D Chapman, Mahmood S Shivji, Ed Louis, Julie Sommer, Hugh Fletcher, Paulo A Prodöhl.

Recommended
- Marine
- Sharks – myths and facts
- Sharks – killers from the depths
- Great white shark
- Megalodon
- Whale shark – largest fish
- Greenland shark
- Longest whales
- Heaviest whales
- Largest sharks
- Extinct animals
- Animal fights
- American lion
- European cave lion
- Smilodon – Saber-toothed tiger
- Fastest animals
- Fastest birds