Aquaponics and Sustainability: Student-Led Initiatives Merging Animal Care with Green Technology
Aquaponics in Academia: How Students Lead in Sustainable Farming Technologies
In the realm of sustainable agriculture, aquaponics emerges as a groundbreaking solution, merging the care of aquatic animals with plant cultivation. This symbiotic system, which combines aquaculture with hydroponics, is gaining traction in academic settings, where students are at the forefront of exploring and refining this eco-friendly technology. Aquaponics represents a holistic approach to farming, addressing issues of water conservation, food security, and environmental sustainability.
In college settings, such projects not only complement academic learning but also offer practical, hands-on experience. These initiatives often become part of coursework, aligning with the growing trend of experiential learning.
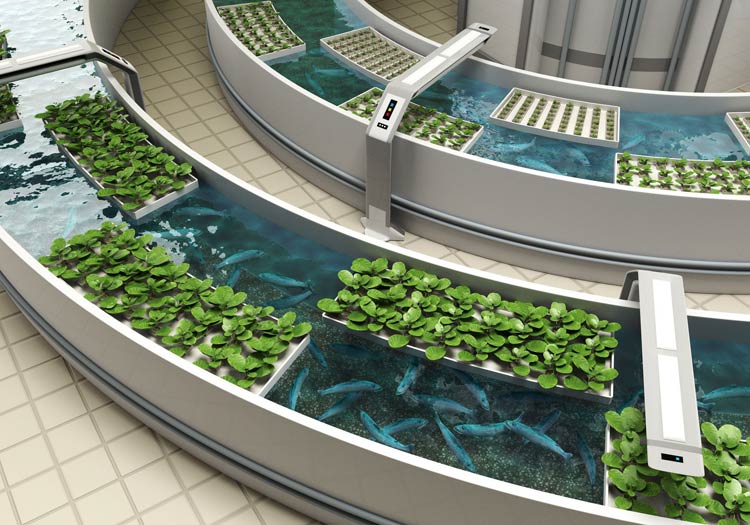

Student-Led Aquaponics Projects: A Hands-On Approach
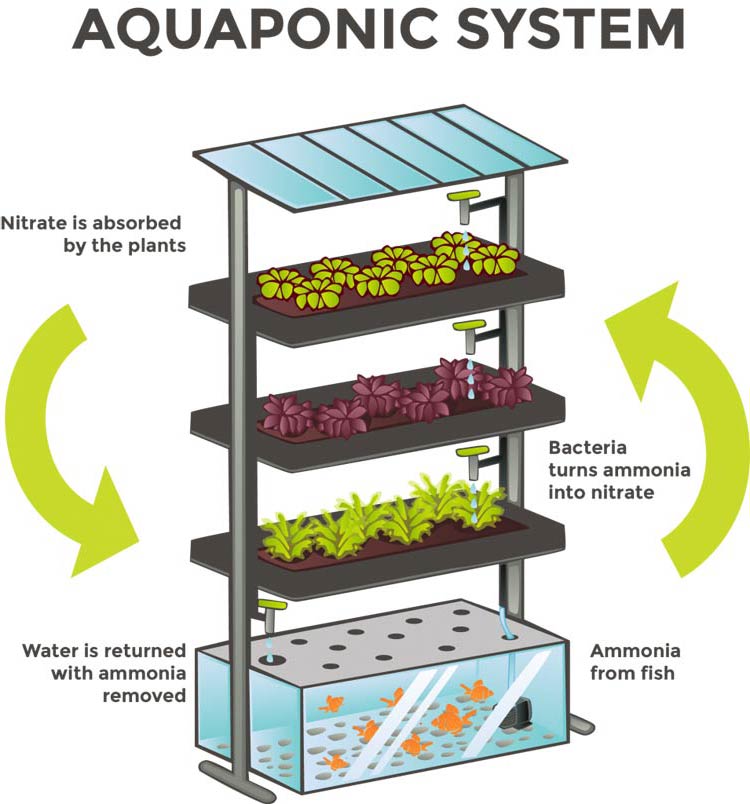
The Basics of Aquaponics
Aquaponics is a progressive and sustainable farming method that combines aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics (soilless plant cultivation). This innovative system forms a mutualistic relationship where fish waste enriches the plants with nutrients, and the plants, in turn, clean and refresh the water that cycles back to the fish habitat. This self-sustaining system is a miniature representation of natural water ecosystems, optimizing the use of resources and reducing waste.
Detailed Process and Ecosystem Balance
In an aquaponics system, the key is to maintain a delicate balance between the fish and plant components. The nitrogen cycle plays a central role, with bacteria converting fish waste into nutrients absorbable by plants. Students learn to monitor and adjust the system parameters, ensuring a healthy environment for both fish and plants, which teaches them about the intricacies of ecological and biological systems.
Implementation in Academic Settings
Aquaponics is becoming a prominent feature in academic landscapes. Colleges and universities are embedding these systems into their science and agriculture programs, giving students a chance to not only learn about sustainable farming but also to get involved in the actual building and management of aquaponics systems. Such projects enable students to translate their theoretical knowledge into tangible applications, effectively narrowing the divide between academic concepts and practical execution.
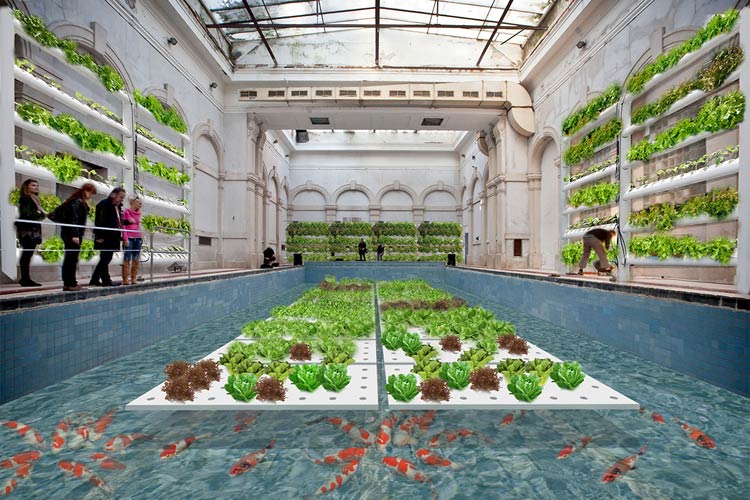

Interdisciplinary Learning and Collaboration
These projects are inherently interdisciplinary, requiring knowledge and skills from various fields such as biology for understanding living systems, engineering for system design, environmental science for sustainability practices, and agriculture for plant and animal care. Participating in these projects broadens the educational scope for students, fostering their skills in interdisciplinary collaboration and teamwork across various academic disciplines.
Benefits of Student Participation
Students participating in aquaponics projects gain hands-on experience in sustainable agriculture practices. They learn about efficient water use, a crucial aspect considering the growing concerns over water scarcity. Additionally, these projects instill in students the importance of resource management and sustainable living practices.
Developing Problem-Solving Skills
As students work on maintaining a balanced aquaponics system, they develop critical problem-solving and analytical skills. They face real-world challenges like pH imbalances, fish health issues, and optimizing plant growth, which require a practical application of their academic knowledge and quick, innovative thinking.
Integrating Technology and Sustainability
Technological Innovations in Aquaponics
In the field of aquaponics, students are leading the way in integrating advanced technological solutions and innovations into these systems. They are integrating IoT (Internet of Things) devices to continuously monitor critical parameters like water quality, pH levels, and nutrient concentrations. The use of sensors and automated systems in aquaponics not only makes maintenance more manageable but also introduces students to the applications of technology in agriculture.
Renewable Energy Integration
There’s a growing trend to power these aquaponics systems using renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power, making the systems even more sustainable. Students explore how to harness and integrate these clean energy sources, further reducing the ecological footprint of their aquaponics projects.
The Role of Data Analytics
The use of data analytics plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and productivity of aquaponics systems, making it a vital component in modern sustainable farming practices. Students utilize data to understand and predict the growth patterns of plants, monitor the health and growth rate of fish, and make informed adjustments to improve the system’s efficiency. This aspect of aquaponics introduces them to the significance of data in environmental and agricultural sciences.

Data-Driven Decisions
The ability to collect and analyze data allows students to make evidence-based decisions, enhancing both the productivity and sustainability of the aquaponics systems. These skills are transferable to various fields, preparing students for data-centric roles in their future careers.
Promoting Eco-Friendly Practices
Student-led aquaponics projects are a platform for advocating environmentally friendly farming practices. Aquaponics exemplifies a method of agriculture that significantly reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, showcasing a path to more sustainable food production methods.
Model for Sustainable Agriculture
By demonstrating the effectiveness of aquaponics in producing food with minimal environmental impact, these projects inspire a broader adoption of sustainable farming practices. They serve as a model for future agricultural innovations focused on sustainability and environmental responsibility.

Challenges and Opportunities
Navigating Practical Challenges
While engaging in aquaponics projects, students often encounter challenges such as balancing nutrient levels, ensuring fish health, and optimizing plant growth. These real-world problems provide a rich learning experience, preparing students for future careers in sustainable agriculture and environmental science.
Future Prospects in Sustainable Agriculture
Aquaponics projects open doors to numerous opportunities in sustainable farming and environmental conservation. Students who participate in these initiatives are well-positioned to lead future advancements in green technology and sustainable food systems.
Conclusion
Aquaponics represents a dynamic and innovative field where student-led initiatives are making significant contributions to sustainable agriculture. By merging animal care with green technology, these projects not only enhance academic learning but also promote real-world applications of sustainability principles. As the demand for sustainable farming practices grows, student involvement in aquaponics stands as a testament to the effective and practical implementation of these principles. For those looking for the best paper writing service in related fields of study, these initiatives offer a wealth of information and inspiration.



















