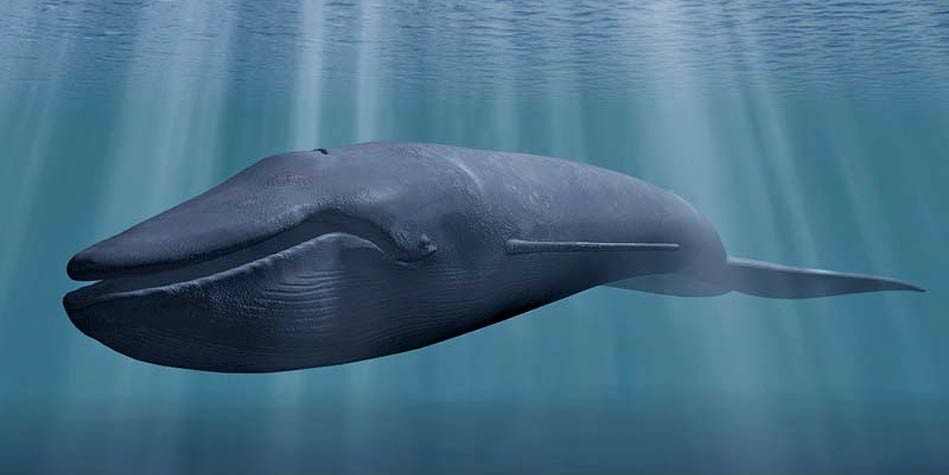
Blue whale (Balaenoptera musculus)
Blue whale is the largest known animal on earth, that ever lived
Whales inhabit all oceans. Just like dolphins they are marine mammals of the Cetacea infraorder. They have no gills so every time they want to breathe in, they have to rise to the surface. Exhaling is accompanied by a spectacular blow, spraying the water upwards.
Most whales does not have teeth. They feed on small sea animals, mainly krill in highly concentrated areas. They find food and maintain spatial orientation through echolocation.
Whales were assumed to be fish for centuries, yet already in 350 B.C. Aristotle pointed out that those animals have no gills, therefore cannot breathe underwater which rules out systematizing them as fish.
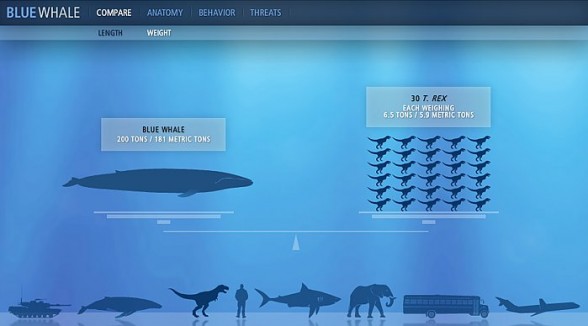
Mammals of the Cetacea infraorder, which count over 80 species, have different coloration, they also vary in size and body shape. Blue whale is the most famous – the largest animal ever to live on our planet. The most magnificent ones reach over 30 meters (98 ft) of length and almost 200 tons of weight. In spite of their enormousness blue whales are not aggressive. Their main food is plankton, which is separated from sea water by special baleen plates. Blue whales generally live a solitary life.

Humpback whale (Megaptera novaeangliae)
Humpback whale is another interesting whale species. Its ill-favored body is covered with lumps, which does not make it visually attractive. Nonetheless it stands out thanks to its highly specialized method of acquiring food. When a humpback encounters a krill swarm it starts to circle below it, exhaling the air from its lungs. Subsequently, the dismayed prey crowds in a small area. The humpback only has to scoop them inside its mouth. These whales have one more fascinating habit. They… sing. Supposedly, their songs even carry a certain melody.
Fat and other substances making up the whales’ bodies are used to produce medication, lubricants and cosmetics, which is why these beautiful animals were killed by thousands not so long ago. Norwegian fishermen even used grenades to hunt them down…

Whale migrations
Whales migrate over the largest distances of all mammals. Whales that spend winters in the warm Pacific waters, breed along the coasts of Mexico. In the summer they swim for over 10 thousand kilometers to Arctic waters, where they are welcomed by the abundance of food. Similar process is observed in case of humpbacks – they spend summer in the North, while in winter they are most often observed in close proximity to Mexico, Hawaii or Bermuda as well as other islands in the warm Caribbean Sea.
A whale fountain
Whales can dive up to 500 meters (1640 ft) deep and stay underwater for two hours. They have to resurface in order to take a breath and restore oxygen reserves in their lungs. Before drawing the first breath, they exhale the air with a considerable power. As a consequence, a distinctive fountain is formed, which may be even 15 meters (49 ft) high. During breath, whales usually pull only their blowholes out of the water, allowing them to exchange the air supply, while the whole body remains submerged.

The whale songs
Whales often wander off the beaten tracks (if any beaten tracks in their case may be considered) Every year they gather in places with the highest food concentration. Whales pass the information about plankton which leads to their rounding up in groups to feast together. Water is a superb sound conductor, hence the major role of hearing and sounds in communication, since sight and smell does not deliver information over great distances.
Although whales do not have vocal cords, they can emit sounds through folds and valves blocking the blowholes, exhaling air through them. This baleen whales’ mechanism is slightly different than the one observed in case of toothed whales. The sounds may resemble singing, clicking, wheezing or gurgling. Not only do they serve as means of communication, but also provide echolocation information (for whales receive the sound waves reflected by objects or sea bottom). Their spatial orientation in the ocean realm is outstanding(as in the case of bats). Echolocation also allows them to find food.
Whales – interesting facts
- The largest whale was stranded on the Grytviken beach (South Georgia, British overseas territory on the Atlantic Ocean) in 1912, it was 33.6 m (110ft 3in) long and weighed 190 tons.
- While exhaling, blue whale sprays up the water up to 15 meters (49 ft) high.
- Whales can dive up to 0.5 km (1640 ft) deep. They can stay underwater for 2 hours straight.
- Blue whales emit sounds audible for other blue whales from 850 km (530 mi).
- Most likely the only natural enemies of whales are giant squids and killer whales.
- Although the blue whale’s brain is large when compared to human’s, it is relatively small regarding its body size.
- Blue whale’s brain has a weight of about 7 kg (6.92 kg) / 15.3lb, which corresponds with only 0.001-0.007% of its total body weight.
- The blue whale’s tongue reaches up to 4 tons of weight (usually around 2.7 tons), while its heart – 600 kg (1323 lb).
- Blue whale’s aorta has a 23 cm (9.1 in) diameter.
- Fully opened mouth of a blue whale is so huge it can hold 90 tons of water and plankton.
- Although its mouth is enormous, its esophagus is relatively narrow. Blue whale cannot swallow any object bigger than a beach ball.
- The newborn blue whale is about 7 meters (22 ft 12 in) long and weighs 2.5 – 2.7 tons.
- During first 7 months the baby blue whale drinks from 380 to 570 liters of mother’s milk every day.
- Blue whale’s milk has a calorific value of 4370 kcal/kg.
- The baby whale gains an average of 4 kilograms (8.8 lb) per hour – about 90 kg (198 lb) every day.
- Blue whale has the largest penis in the animal kingdom. Its organ reaches from 2.4 to 3 meters (7 ft 10 in – 9 ft 10 in) of length.
- Blue whale’s daily calorie intake is 1.5 million kcal.
- A blue whale can eat up to 3.6 tons of food over the day.
- Largest whales can swim almost 40 km/h (25 mph).
- Some whales can jump above the water surface, like killer whales or dolphins.
- One of the whale species, the sperm whale, hunts by stunning its prey with a sound wave.

Detailed characteristic / size
Blue whale (Balaenoptera musculus)
- Length: up to 34 m (111 ft), the largest recorded whale, stranded on Grytviken in 1912 was 33.6 m long (110ft 3in)
- Weight: up to 190 tons
- Coloration: blue to gray, skin speckles sporadically
- Food: fish, mollusks, crustacean, zooplankton.
- Maturity: after reaching 20 meters of length.
- Breeding: pregnancy lasts about 11 months, newborn are approximately 7 m (22 ft 12 in) long and weighs 2,700 kg, gaining 4 kg of weight an hour for its first 9 months.
- Speed: up to 30 km/h.
- Lifespan: 80 years.



















