Evolution theory – what is evolution?
What is evolution?
The theory of evolution states that species change over time. There are many different ways to change species, but most can be described by the idea of natural selection. The theory of evolution describing these changes as occurring by natural selection was the first scientific theory to gather evidence of changes over time and describe the mechanism of their formation.
History of the theory of evolution
The idea that traits are passed down from parents to offspring has been around since the times of ancient Greek philosophers. In the middle of the 18th century, Carl Linnaeus (Carolus Linnaeus) developed his taxonomic naming system in which he grouped species together and suggested that there was an evolutionary relationship between species within the same group. The taxonomic system he created has become the foundation of modern taxonomy.
In the late 18th century, the first theories emerged that species change over time. Scientists such as Comte de Buffon and Charles Darwin’s grandfather, Erasmus Darwin, have suggested that species change over time, but neither has been able to explain how or why they changed. Both kept their reflections secret, due to their controversy with the prevailing religious views.
John Baptiste Lamarck, a student of Count Buffon, was the first to publicly state that species change over time. However, part of his theory was incorrect. Lamarck proposed that acquired traits are passed on to offspring. Georges Cuvier has shown that this part of Lamarck’s theory is wrong, but he also had evidence that there once lived species that evolved and died out.
Cuvier believed in a catastrophe, which meant that these changes and extinctions in nature happened suddenly and violently – see extinction. James Hutton and Charles Lyell opposed Cuvier’s argument with the idea of uniformitarianism. This theory says that changes occur slowly and accumulate over time.
Darwin and natural selection
Natural selection, sometimes called “survival of the fittest,” was explained and made famous by Charles Darwin in his book, “On the Origin of Species”, published in 1859.
In his book, Darwin suggested that individuals with the traits most appropriate to their environment lived long enough to pass on these desirable traits to their offspring. If an individual did not have favorable traits, he would die without passing them on. Only the “strongest” traits for a given species have survived over time. Eventually, after sufficient time had passed, these little adaptations would add up to form new species. These changes make us the people we are.
Darwin was not the only one to come up with the idea at the time. Alfred Russel Wallace also had the evidence and came to the same conclusions as Darwin at the same time. The two gentlemen collaborated for a short time and presented their findings together. Armed with evidence from around the world, amassed over numerous journeys, Darwin and Wallace received positive reviews from the scientific community. However, the collaboration ended when Darwin published his book.
A very important part of the theory of evolution, which happens through the mechanism of natural selection, is the understanding that individuals cannot evolve; they can only adapt to their own environments. These adaptations add up over time and eventually the entire species evolves. This can lead to the formation of new species and sometimes the extinction of existing ones.

Evidence for Evolution
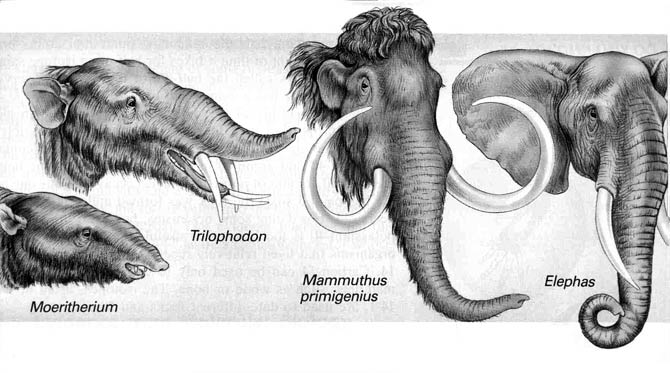
There is ample evidence to support the theory of evolution. Darwin relied on the similar anatomy of species to bring them together. It also had some fossil evidence that showed little changes in the body structure of the species over time, often leading to vestigial structures. Of course, the fossil record is incomplete and contains “missing links”.
With today’s technology, there are many other types of evidence for evolution. This includes the embryo similarities between different species, the same DNA sequences found in all species, and an understanding of how DNA mutations work in microevolution. More fossil evidence has also been discovered since Darwin’s time, although there are still many gaps in the fossil record.

The controversy around the theory of evolution
Today, the theory of evolution is often presented in the media as a controversial topic. The evolution of primates and the idea that humans evolved from apes have been a major point of friction between scientific and religious communities. Politicians and the judiciary wondered whether schools should teach evolution or whether they should teach alternative viewpoints such as creationism or intelligent design (ID).
In 1925, teacher John Scopes was arrested for illegally teaching evolution at a school in Tennessee (USA). It was the first major judicial battle over evolution to bring attention to a topic formerly considered taboo.

The theory of evolution in biology
The theory of evolution is often seen as the theme that encompasses all branches of biology. It includes genetics, population biology, anatomy and physiology, and embryology, among others. While the theory itself developed over time, the principles set out by Darwin in the 19th century are still valid today.

The theory of evolution – trivia
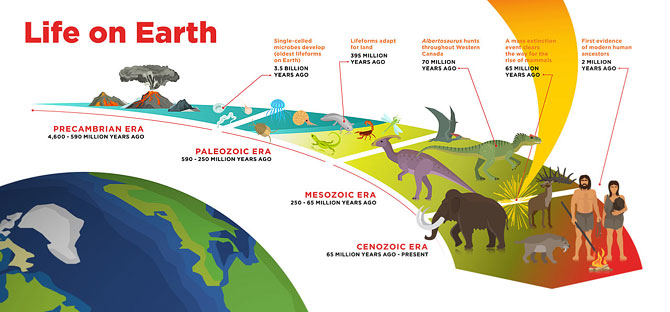
- All life on Earth today is assumed to come from a common ancestor.
- The common ancestor of all living organisms today lived about 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. In 2015, remains that may be the remnants of life from 4.1 billion years ago, found in rocks in Australia, were described.
- Currently, there are 10-14 million species on Earth, 1.2 million of which have been described so far.
- In the early 1900s, an evolutionary synthesis was performed, integrating classical genetics with Darwin’s theory of evolution.
- The idea that organisms of one kind could have been derived from organisms of a different kind arose in ancient Greece by thinkers such as Anaximander and Empedocles. These views survived to Roman times.
- Organisms evolve through changes in features that are inherited (known as hereditary features).
- Hereditary features are transferred from generation to generation through DNA, which acts as a carrier of genetic information in living organisms.
- Mutations are changes to the DNA sequence. A mutation may change the product of the gene, prevent the gene from functioning, and may not have any effect.